The Horten Ho XVIII actually were 3 different projects made by Horten brothers in 1944 in order of RLM requirement for an aircraft with a range of 11000 km (6835 miles) and a bomb load of 4000 kg (8818 lbs). None of aircraft ever archived like that. Five of Germany's top aircraft companies had submitted designs, but none of them met the range requirements for this Amerika Bomber. Horten are one of these company The Hortens were not invited to submit a proposal because it was thought that they were only interested in fighter aircraft.
The Horten brothers realised the failures and redesign the aircraft modified with 6 jumo 004 turbojet and 2 mg turret to protect the aircraft. When the meeting with Messerschmitt and Junkers engineers were helded. These engineers feel unsatsifactory with the first design-the Ho XVIIIa. After that Reimar-one of the Horten brothers feel unhappy and redeisgn it again with 2x He S011 jet engines in each of two fixed main landing gear assemblie. The prototype was proposed to test in the end of 1945 but the Allies advance was too fast and in May 1945, German surrender ended the project
This site is about unbuilt and cancelled aviations projects. It provides you with info about these projects like specifications, history, etc. And also talks about avionics like engines, armaments for military aircrafts, and equipments like radar, nuclear reactor, etc.
Monday, July 5, 2010
Focke Wulf P II jet project
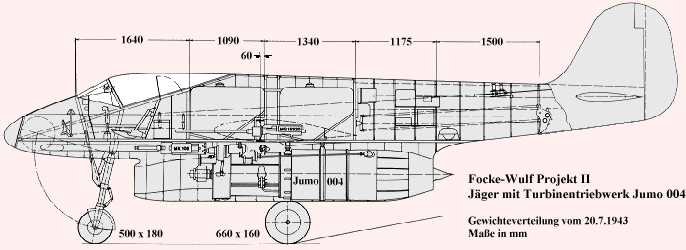
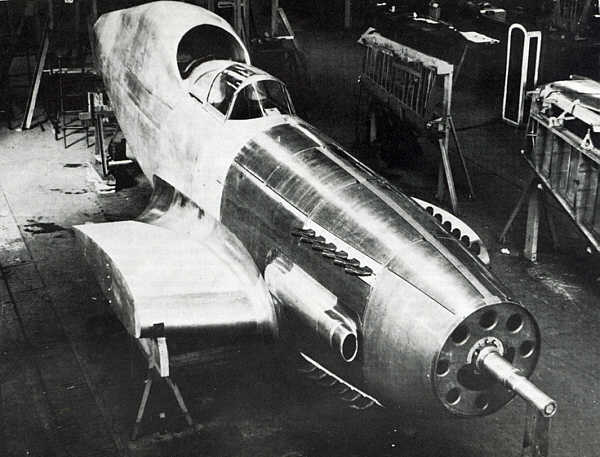
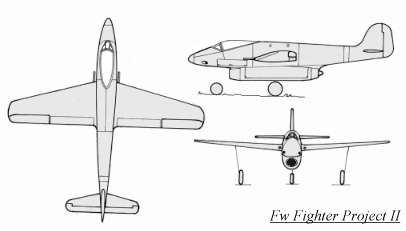 The P II was a second of the Kurt Tank jet fighter project which was intended to give to the RLM(Reich air ministry) in 1943. The wings were mounted mid-fuselage and had a slight sweep on the leading edge and straight trailing edges. A single Jumo 004B turbojet were slung beneath the fuselage The main advantage was to facilitate maintenance.But there are many other disadvantages on this design, such as the nose wheel blocking the intake on takeoff and landing, foreign matter being sucked into the intake since it was so close to the ground and the destruction of the jet engine in case of a belly landing.Armarments considered to be 2x MK 108 cannons in the nose and 2x MG151 in the wing roots. Because of it disadvantages the project was not followed up and cancelled
The P II was a second of the Kurt Tank jet fighter project which was intended to give to the RLM(Reich air ministry) in 1943. The wings were mounted mid-fuselage and had a slight sweep on the leading edge and straight trailing edges. A single Jumo 004B turbojet were slung beneath the fuselage The main advantage was to facilitate maintenance.But there are many other disadvantages on this design, such as the nose wheel blocking the intake on takeoff and landing, foreign matter being sucked into the intake since it was so close to the ground and the destruction of the jet engine in case of a belly landing.Armarments considered to be 2x MK 108 cannons in the nose and 2x MG151 in the wing roots. Because of it disadvantages the project was not followed up and cancelledReferences
http://www.luft46.com/fw/fwpiib.html
Diagram of the P II
Arsenal VB-10
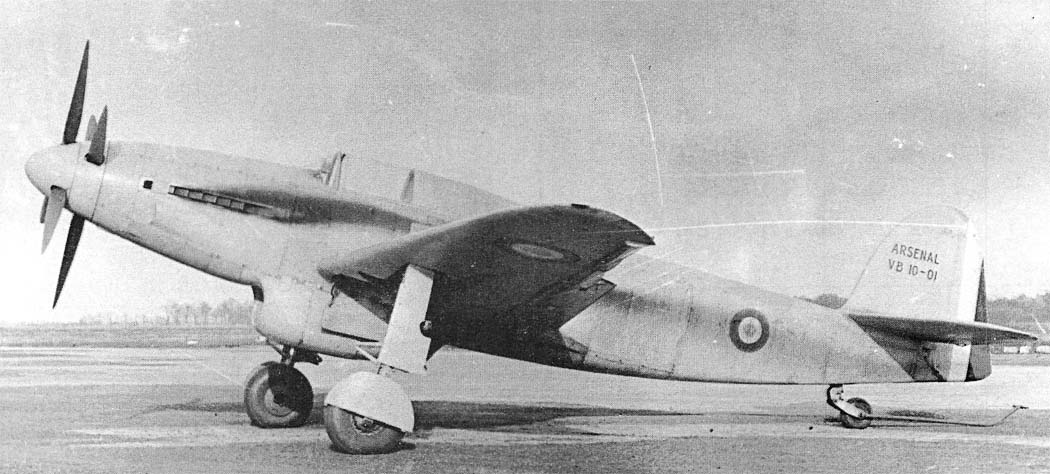
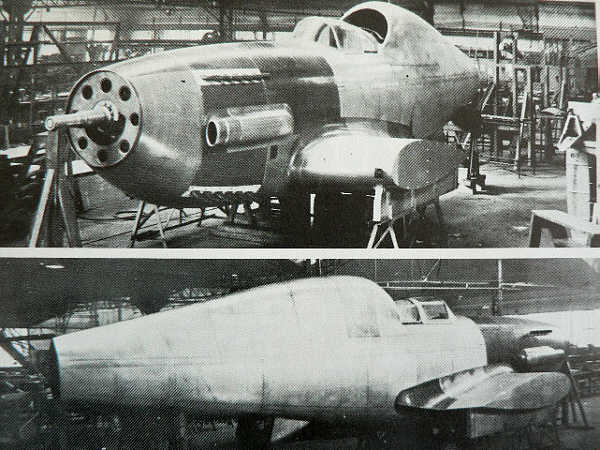
The Arsenal VB-10 was a French Tandem engines fighter prototypes developed during and shortly after World War II. It was a monoplane with largely orthodox configuration and retractable tailwheel the VB 10 added a second engine behind the cockpit which drove a second propeller, coaxial with and counter-rotating to the propeller driven by the engine in the nose. Although the aircraft was first designed (and indeed ordered) in 1940, but because of French occupation, the aircrafts could not flown until Europe was freed .But then, the Amee de air changed their favor on the jet technology and age of piston engine was over so the project was cancelled in 1948 and all 6 prototypes were scrapped.
Specification
General characteristics
Specification
General characteristics
- Crew: one, pilot
- Length: 12.98 m (42 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 15.49 m (50 ft 10 in)
- Height: 5.2 m (17 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 35.5 m² (382 ft²)
- Powerplant: 2 × Hispano-Suiza 12Zars-15/16, 860 kW (1,150 hp) each
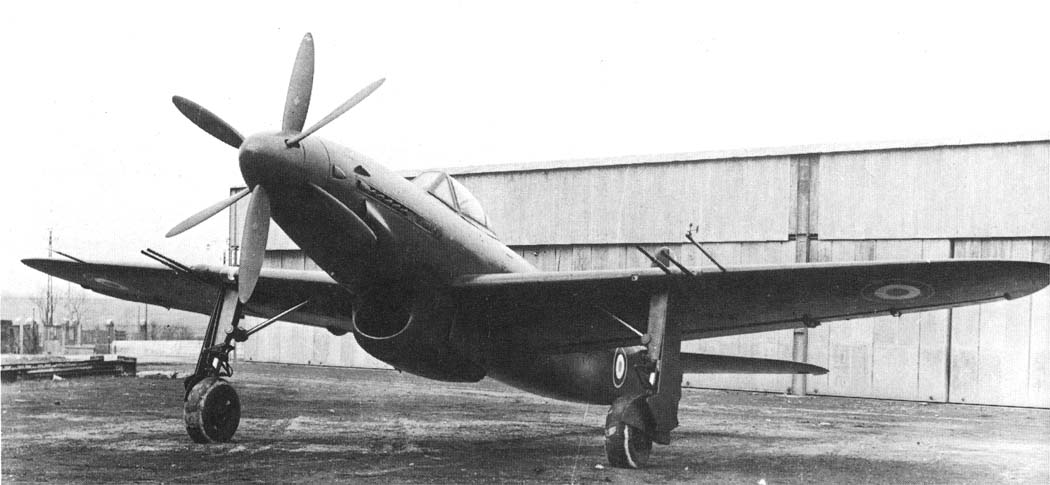

- Maximum speed: 700 km/h (435 mph)
- Range: 7,700 km (1,056 miles)
- Service ceiling: 11,010 m (36,120 ft)
- Rate of climb: 10.2 m/s (2,008 ft/min)
- 4 × 20 mm Hispano Suiza HS-404 cannons
Sunday, June 27, 2010
Dornier Do 214 heavy flying boat project
 Dornier Do 214 is a multi purpose flyingboat originally designated number P 93 for a heavy transporter at first. The Göppingen Gö 8 were used to test for the project .Proposed powerplants were to be 8x Daimler Benz DB 613 piston engines.The front propellers had a 5.0 m (16' 5") diameter, the rear had a 4.6 m (15' 1") diameter. The rear propellers were driven by an extension shaft and were also hinged, which allowed the rear propellers to be raised during takeoff for water clearance . Fuel capacity consisted of 66000 liters in the huge fuselage and 1500 liters contain in each wing.A single fin were added and all 8 engines were monitored by a flight engineer from the central station .The Airliner variant crew are twelve men: a captain, two pilots, navigator, radio operator, two flight engineers, two stewards, two hostesses, and one crew member held in reserve and forty passengers could be carried in comfort and 2.6 tons of freight and luggage could be carried in the lower fuselage storage area. In 1943, a mockup was reconstructed to investigate the best placement of the gun turrets and other military stores but then the flying boat was no longer needed due to worsening war situation.
Dornier Do 214 is a multi purpose flyingboat originally designated number P 93 for a heavy transporter at first. The Göppingen Gö 8 were used to test for the project .Proposed powerplants were to be 8x Daimler Benz DB 613 piston engines.The front propellers had a 5.0 m (16' 5") diameter, the rear had a 4.6 m (15' 1") diameter. The rear propellers were driven by an extension shaft and were also hinged, which allowed the rear propellers to be raised during takeoff for water clearance . Fuel capacity consisted of 66000 liters in the huge fuselage and 1500 liters contain in each wing.A single fin were added and all 8 engines were monitored by a flight engineer from the central station .The Airliner variant crew are twelve men: a captain, two pilots, navigator, radio operator, two flight engineers, two stewards, two hostesses, and one crew member held in reserve and forty passengers could be carried in comfort and 2.6 tons of freight and luggage could be carried in the lower fuselage storage area. In 1943, a mockup was reconstructed to investigate the best placement of the gun turrets and other military stores but then the flying boat was no longer needed due to worsening war situation.Specification
Span:60 m
Length:51.6 m
Height:14.3 m
Wing Area:500 m²
Empty Weight:76000 kg
Loaded Weight :145000 kg
References:http://www.luft46.com/dornier/do214.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dornier_Do_214
Monday, June 21, 2010
Boulton Paul P 100
 Boulton Paul P 100 is a projected ground attack aircraft submitted by Boulton Paul in response to Specification F. 6/42 which called for a 'single seat low level attack aircraft'. The P.100 was an innovative and forward-thinking design with features that were maybe too advanced for the time such as the unique 'jaw' at the nose which allowed the pilot to escape without danger of hitting the pusher propeller. But later in January 1944, the RAF want to terminated the project because it role already exist on 3 aircraft: the Hawker Typhoon, Tempest and Hurricane.
Boulton Paul P 100 is a projected ground attack aircraft submitted by Boulton Paul in response to Specification F. 6/42 which called for a 'single seat low level attack aircraft'. The P.100 was an innovative and forward-thinking design with features that were maybe too advanced for the time such as the unique 'jaw' at the nose which allowed the pilot to escape without danger of hitting the pusher propeller. But later in January 1944, the RAF want to terminated the project because it role already exist on 3 aircraft: the Hawker Typhoon, Tempest and Hurricane.Specification
- Powerplant:1x Rolls Royce Griffon II driving contra rotating props
- Span :12.2m
- Length:10.4m
- Max speed:571 Km/h
- Service range:5,182m
- Proposed armament :4 x 20mm Cannon or 2 x 40mm + 2 x 20mm canon ,one 47mm Vickers cannon
- Ornances:8 x RP3 Rockets,2 x 500 lb. bombs
Dewoitine /Sud Est SE 580
In 1944, when France been freed , the Aeronautic Manufacturing National Societies or SNCA try to built a new type of fighter based on the project of the SNCA du Midi M 580-an early design of SE 580 in 1940, the SE 580 wing planform-with its near mid-chord single spar and its empennage surfaces planforms-was similar to the D520, albeit the horizontal planes had slightly greater aspect ratio. Initially designed to be powered by the 24-cylinder Hispano Suiza 24Z (H type) of 2,000hp, its postwar redesign accommodated the 24-cylinder arsenal 24 H of 3,400hp. This latter engine used the cylinder blocks of the German Junkers IV12 213 engine.
Two 12.1-foot-diameter coaxial, counter-rotating propellers were to be utilized for propulsion.
 It was to be armed with a 30mm cannon firing through the propeller axis, plus four 20mm cannon and either eight 7.Smm or six 12.7mm machine guns mounted in the wings outboard of the propeller arc. A 500kg (1,100 lb.) bomb could be carried beneath the fuselage. It is obvious that the after-cockpit buried radiator with top-mounted radiator intake was for protection from ground fire.
It was to be armed with a 30mm cannon firing through the propeller axis, plus four 20mm cannon and either eight 7.Smm or six 12.7mm machine guns mounted in the wings outboard of the propeller arc. A 500kg (1,100 lb.) bomb could be carried beneath the fuselage. It is obvious that the after-cockpit buried radiator with top-mounted radiator intake was for protection from ground fire.One thing was sure is 2 prototypes were ordered but they were not complete because the project was cancelled when the Amee de Air( French airforce) focus more on jet fighters along with it competitor-the Arsenal VB-10 shortly thereafter.
Specification
- Powerplants:Hispano Suiza 24Z(2x Hispano Suiza 12Z)
- Armaments:30mm cannon in the props axis, 2x HS 404 cannons in each wing
- Propellers:6 blades contra rotating props or 5 blades counter rotating prop
- Span 15.862m
- Length 13.000m
- Weight 5093kg
- Maximum speed 749km/h
Monday, June 14, 2010
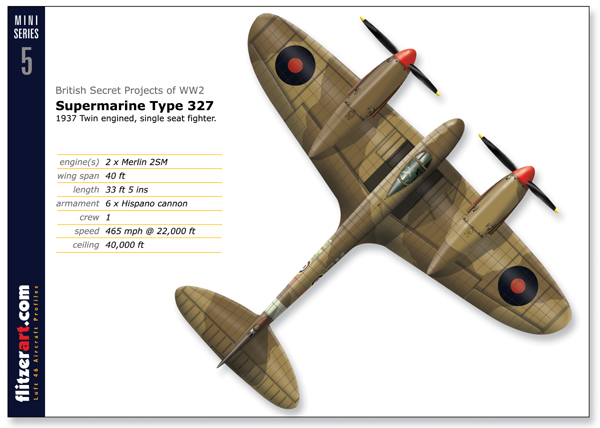
Supermarine type 327 Spito
The Supermarine type 327 is a proposed twin engineed version of the successful Spitfire which was entered production later. A mock up were built for testing but later it was destroyed in fire when it was in factory.In fact it was to a design spec requested by the Air Ministry to actually replace the Spitfire which was entering service.
The 327 was an improvement version of type 324 with 6 cannons in wing root for replace 12 MG in type 324 wings.
Artwork for type 327 Spito
The 327 was an improvement version of type 324 with 6 cannons in wing root for replace 12 MG in type 324 wings.
Artwork for type 327 Spito
- Powerplants:2x Rolls Royce Merlin 25M
- Wingspan:40 feet
- Length:33feet 5 inch
- Armarment:6x Hispano Suiza HS 404 cannons
- Crew:1(pilot)
- Speed:465mph
- Ceiling:40000feet
Monday, June 7, 2010
Roll Royce Medway
Roll Royce Medway is a proposed large low-bypass turbofan engine produced by Roll Royce and tested in early 1960s. The project was cancelled due to favor of the Roll Royce Spey engine and the cancellation of Armstrong Whitworth AW.681 VTOL transporter project.
 The development of this engine were based on the Roll Royce Pegasus engine which were used for Harrier prototype, it was designed byby a team led by Alan Arnold Griffith, the RB.141 was originally designed to meet a new propulsion requirement for the de HavillandDH.121 airliner project which later became the Hawker Siddeley Trident. The engine was later named after the River Medway in line with Rolls-Royce company tradition for jet engines.
The development of this engine were based on the Roll Royce Pegasus engine which were used for Harrier prototype, it was designed byby a team led by Alan Arnold Griffith, the RB.141 was originally designed to meet a new propulsion requirement for the de HavillandDH.121 airliner project which later became the Hawker Siddeley Trident. The engine was later named after the River Medway in line with Rolls-Royce company tradition for jet engines.
The first application for the medway is the Armstrong Whitworth AW 681 VTOL transporter prototype.
The rear section of the engine was modified to incorporate an internal thrust deflector to duct exhaust gases through swivelling nozzles; an idea similar to that used on the contemporaryBristol Siddeley Pegasus. Cancellation of the AW.681 project however also brought to an end further development work on the Medway with attention turning to the smaller, but very closely related, Spey turbofan.
Another application is for the SAAB Vigen, the Sweden military attack aircraft but due to government funding, the idea was not adopted.
In December 1963 the Medway had successfully completed over 1,700 hours of bench running.
 The development of this engine were based on the Roll Royce Pegasus engine which were used for Harrier prototype, it was designed byby a team led by Alan Arnold Griffith, the RB.141 was originally designed to meet a new propulsion requirement for the de HavillandDH.121 airliner project which later became the Hawker Siddeley Trident. The engine was later named after the River Medway in line with Rolls-Royce company tradition for jet engines.
The development of this engine were based on the Roll Royce Pegasus engine which were used for Harrier prototype, it was designed byby a team led by Alan Arnold Griffith, the RB.141 was originally designed to meet a new propulsion requirement for the de HavillandDH.121 airliner project which later became the Hawker Siddeley Trident. The engine was later named after the River Medway in line with Rolls-Royce company tradition for jet engines.The first application for the medway is the Armstrong Whitworth AW 681 VTOL transporter prototype.
The rear section of the engine was modified to incorporate an internal thrust deflector to duct exhaust gases through swivelling nozzles; an idea similar to that used on the contemporaryBristol Siddeley Pegasus. Cancellation of the AW.681 project however also brought to an end further development work on the Medway with attention turning to the smaller, but very closely related, Spey turbofan.
Another application is for the SAAB Vigen, the Sweden military attack aircraft but due to government funding, the idea was not adopted.
In December 1963 the Medway had successfully completed over 1,700 hours of bench running.
Specifications (RB.141-3 Medway)
General characteristics
- Type: Low bypass twin-spool turbofan
- Length:
- Diameter:
- Dry weight:
Components
- Compressor: Axial, 5-stage LP, 11-stage HP
- Combustors: Cannular, 10 chambers
- Turbine: 2-stage LP, 2-stage HP
Performance
- Maximum thrust: 11,800 lb
- Overall pressure ratio: 16.75:1
- Power-to-weight ratio:unknown
Curtiss XP-71
 Curtiss XP-71 was a 1940 proposal of a heavy escort fighter aircraft for USAAF. It was equipped with a pressurized cockpit and equipped with two Pratt and Whittney Wasp Mayor radial engines. It featuring the pusher configuration with 8 countra rotating propellers. Based on the experience of heavy fighter, these type of aircrafts were requested as escort for bombers. Two prototypes were ordered. The development were equipped with Wasp Mayor turbocharged radial engines was supposed to be the biggest aircraft during the war
Curtiss XP-71 was a 1940 proposal of a heavy escort fighter aircraft for USAAF. It was equipped with a pressurized cockpit and equipped with two Pratt and Whittney Wasp Mayor radial engines. It featuring the pusher configuration with 8 countra rotating propellers. Based on the experience of heavy fighter, these type of aircrafts were requested as escort for bombers. Two prototypes were ordered. The development were equipped with Wasp Mayor turbocharged radial engines was supposed to be the biggest aircraft during the warThe final design of the XP-71 was bigger than the B-25 Mitchell medium bomber so this complex aircraft was considered to be need a lot of resources to built. A mock up was built to gained data for the prototypes but later, the requirement of more advanced fighters such as jets led to the cancellation of the XP-71 project and the prototype was never built in 1942.
Specification
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 61.83 ft (18.85 m)
- Wingspan: 82.25 ft (25.07 m)
- Height: 19.0 ft (5.79 m)
- Wing area: 602 ft² (55.9 m²)
- Empty weight: 31,060 lb (14,090 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 46,950 lb (21,295 kg)
- Powerplant: 2× Pratt & Whitney R-4360-13 "Wasp Major" radial engines, 3,450 hp (2,574 kW) each
- Maximum speed: 428 mph (371 knots, 690 km/h) at 25,000 ft (7,620 m)
- Range: 3,000 mi (2,600 nm, 4,800 km)
- Service ceiling: 40,000 ft (12,192 m)
- Max wing loading: 51.6 lb/ft² (252 kg/m²)
- Minimum power/mass: 0.147 hp/lb (242 W/kg)
- Time to altitude: 12.5 min to 25,000 ft (7,620 m)
- Guns:
- 1× 75 mm (2.95 in) cannon
- 2× 37 mm (1.46 in) cannon
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curtiss_XP-71
Monday, May 31, 2010
General Electric YJ93
The General Electric YJ93 was a turbojet engine design for the XB-70 and XF-108 project. The engine was a single shaft axial flown turbojet with a variable stator compressor and a fully-variable convergent/divergent exhaust nozzle. The maximum sea-level thrust was 28,800 lbf. he YJ93 started life as the General Electric X275, an enlarged version of the J-79 tturbojet. This evolved to the X279 when Match 3 cruise became a requirement, and ultimately became the YJ93.
The engine used a special high-temperature JP-6 fuel. The six YJ93 engines in the XB-70 Valkyrie were capable of producing a thrust to weight ratio of 5, allowing for a speed of 2,000 mph (approximately Mach 3) at an altitude of 70,000 feet.
After the cancellation of XF-108 program, the XB-70 was turned into research project and one of the engine was put into museum exhibit.
Specification
The engine used a special high-temperature JP-6 fuel. The six YJ93 engines in the XB-70 Valkyrie were capable of producing a thrust to weight ratio of 5, allowing for a speed of 2,000 mph (approximately Mach 3) at an altitude of 70,000 feet.
After the cancellation of XF-108 program, the XB-70 was turned into research project and one of the engine was put into museum exhibit.
Specification
- TSFC dry: 0.700 lb/(lb.h)
- TSFC wet: 1.800 lb/(lbf.h)
- Core airflow: 275 lb/s
Monday, May 24, 2010
Antonov Istrebitel
In 1944, Antonov was impressed by Heinkel He 162 jet fighter from Germany. So he tried to made his own design of a superior fighter with a single RD-10 turbojet. The armarments was to be 2x NK-23 cannons in nose. The cockpit seemed to be like P-39 Aircobra because it have an openable door. Later, Soviet requires of a jet fighter, so the project were given the number An-2 or SKh. But later, the new jet fighter with better configuration,the Yakolev Yak 10 was flown and tested with the same engine and weapons but more performance so the project of Antonov were no more than the wind tunnel model and cancelled.
Istrebitel windtunnel model
- Powerplant: 1x RD-10 axial flown turbojet
- Armarment: 2x NK-23 30mm cannon
- Span:10,8m
- Length:10,6m
- Max Speed: about 900km/h
- Crew:1 pilot
Douglas XB-31
The Douglas XB-31 was a was the design submitted by Douglas aviation company to US army air corp as a requirement of a long range heavy bombers. Around 1938, United States Army General Henry H. 'Hap' Arnold, the head of the Army Air Force, was growing alarmed at the possibility of war in Europe and in the Pacific. Hoping to be prepared for the long-term requirements of the Air Force ,Arnold created a special committee chaired by Brigadier General W. G. Kilner;,one of its members was Charles Lindbergh. After a tour of Luftwaffe bases, Lindbergh became convinced that Nazi Germany was far ahead of other European nations. Despite the promising design, it never progressed past the design stage, the reason is because the Boeing B-29 was already chosen to be main heavy bomber for Pacific theatre.
Specifications
- Crew: 8 (2 pilots, 4 gunners, 1 radioman, 1 radar technician)
- Length: 35,7m
- Wingspan:63.1 m
- Height:12,99m
- Wing area:310m²
- Empty weight:49,530 kg
- Loaded weight:60,870 kg
- Take off weight:89,800 kg
- Powerplant: 4x Pratt & Whittney Wasp Mayor radials
- Max speed:357mph
- Range:3000 miles
Myasischev M-50 Bounder
In 1955,the Myasischev OKB(bureau) has headed toward on a research to built a supersonic bomber. The archives of the design were the dash attacks,fast bombing, nuclear bomber.The project was begun in 1955 and 2 protypes were ordered from Soviet airforce.Many designs were made until they have a new designs
. The design name's M-50 for first prototype. 2 prototypes were built but only one of them, the M-50 were flown because the project was cancelled later. Even the project was cancelled, the M-50 still have a decision to made it final flight in Tushino show. Another prototype for M-50 project, the M-52 also built as a nuclear bomber but after the project cancelled the aircraft complete but it was never have flight test and scrapped . There are also many other projects about the M-52 with other configuration but they were never built.Later it was received considerable attention from westerns observers and was given the NATO name's Bounder and presented at Tunisho show for now.
Description
Designer : OKB V.M.Myasishchev
NATO code name; Bounder
Role:Strategical supersonic bomber
Crew:2 pilots
Specification
1.M-50A
General characteristics
2.M-52A
Pictures
M-50 drawings
M-50 for today
M-52 wind tunnel models
M-52 prototype awaiting for test flight
M-50 in flight
. The design name's M-50 for first prototype. 2 prototypes were built but only one of them, the M-50 were flown because the project was cancelled later. Even the project was cancelled, the M-50 still have a decision to made it final flight in Tushino show. Another prototype for M-50 project, the M-52 also built as a nuclear bomber but after the project cancelled the aircraft complete but it was never have flight test and scrapped . There are also many other projects about the M-52 with other configuration but they were never built.Later it was received considerable attention from westerns observers and was given the NATO name's Bounder and presented at Tunisho show for now.
Description
Designer : OKB V.M.Myasishchev
NATO code name; Bounder
Role:Strategical supersonic bomber
Crew:2 pilots
Specification
1.M-50A
General characteristics
- Crew: Two
- Length: 57.48 m (188 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 35.10 m (115 ft 2 in)
- Height: 8.25 m (27 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 290.6 m² (3,128 ft²)
- Empty weight: 85,000 kg (187,000 lb)
- Loaded weight: 175,000 kg (386,000 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 200,000 kg (440,000 lb)
- Powerplant: 2× Dobrynin VD-7M afterburning turbojets, 156.9 kN (35,270 lbf) each, and 2× VD-7B turbojets, 92.12 kN (20,710 lbf) each
- Maximum speed: 1,950 km/h (1,210 mph)
- Cruise speed: 1,500 km/h (930 mph)
- Range: 7,400 km (4,600 mi)
- Service ceiling: 16,500 m (54,100 ft)
- Rate of climb: m/s (ft/min)
- Wing loading: 602 kg/m² (123 lb/ft²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.29
- 30,000 kg (66,000 lb) of bombs or missiles carried in internal bay
2.M-52A
- Length:57,48m
- Overall height:8,25m
- Wing Span: 25,1m
- Wing Area:290,63 m2
- Take-off weight: 115000kg
- Weight:78860 kg
- Engines:2 VD-7B + 2 VD-7 turbojet engines
- Speed:1050 km/h
- Practical range: 3150km
- Practical ceiling: 11000m
- Landing run:1800m
Pictures
M-50 drawings
M-50 for today
M-52 wind tunnel models
M-52 prototype awaiting for test flight
M-50 in flight
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)